Ag/Cu co-doped ZnS–In2S3 solid solutions: facile synthesis, theoretical calculations and enhanced photocatalytic activity†
Abstract
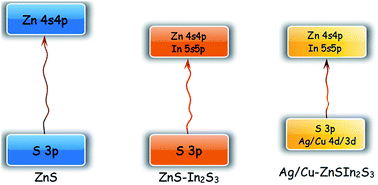
ZnS–In2S3 nanospheres were prepared by a simple hydrothermal method without using any organic solvents or templates. In order to improve the photocatalytic performance, Ag and Cu were chosen as doping elements for both single-doping and co-doping. The band structure, electronic structure and electron density were carefully investigated based on density functional theory (DFT). The roles of In and Ag/Cu in the solid solutions are found to be band adjustment, electron density control and electron mobility optimization due to the d orbitals of Ag and Cu. A series of photocatalysts were further characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV-visible diffuse reflectance spectra (UV-vis) and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area measurement. It is found that the formation of a solid solution greatly broadened the light response range and made visible light response possible. When the amounts of Ag and Cu are 0.2 mL and 0.3 mL, the Ag/Cu co-doped ZnS–In2S3 solid solution showed the optimized value of 2.15 mmol h−1 g−1 under visible-light irradiation without using any noble metal as a co-catalyst. After four cycles of photocatalytic tests, the activity barely decreased.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...