Zinc–bromine hybrid flow battery: effect of zinc utilization and performance characteristics
Abstract
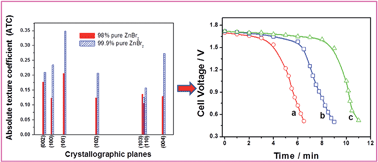
In order to achieve maximum efficiency and long lifetime of a zinc–bromine flow battery (ZBB), the deposition and dissolution of zinc during the charging and discharging processes, respectively, need to be in balance. In view of this, the percentage utilization of zinc during the discharge process was investigated in a zinc–bromine redox flow cell through a potentio/galvanodynamic polarization test and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The cell employed carbon–plastic composite electrodes and 98% pure zinc bromide electrolyte solution. The zinc–bromine cells were charged at various current densities of 10, 20 and 30 mA cm−2, and the deposited Zn during charging was compared with the dissolved zinc during the discharge process and found to be 39, 41 and 39%, respectively. A 10% increase in the zinc utilization factor was observed, and this resulted in a 17% increase in the Faradaic efficiency when 99.9% pure zinc bromide electrolyte solution was used. At the same time, 50% utilization of zinc resulted in a further 20% increase in Faradaic efficiency in a cell with non-porous graphite electrodes and 98% pure zinc bromide salt solution. To qualify the nature of the Zn deposit, XRD analysis was carried out along with other spectral studies. The basal plane of zinc (002) was observed at a lower intensity peak, whereas the plane (101) showed preferential growth in the (101) direction. From these spectra, grain size and texture coefficient (TC) were also calculated in order to realize better Zn utilization in a zinc–bromine hybrid flow cell.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...