Photoelectrochemical activity of ZnFe2O4 modified α-Fe2O3 nanorod array films†
Abstract
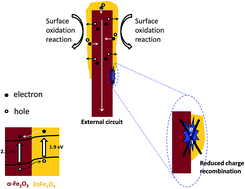
ZnFe2O4 modified α-Fe2O3 nanorod array films were successfully synthesized by aqueous solution growth followed by a spin coating process and studied for photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting under solar light. Through the spin coating process, ZnFe2O4 was found mainly to exist at the top surface of the α-Fe2O3 nanorod arrays. After being modified by ZnFe2O4, the α-Fe2O3 nanorod film was identified as a suitable surface treatment, and showed an increased photocurrent density when used as the photoanode. It was demonstrated that ZnFe2O4 increased the charge carrier density and acted as the oxidation cocatalyst. These results suggested that surface treatment by ZnFe2O4 should be a practical strategy to improve the efficiency of α-Fe2O3 or other metal oxide photoanodes for PEC solar fuel conversion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...