Synthesis and biological evaluation of quinoline–imidazole hybrids as potent telomerase inhibitors: a promising class of antitumor agents
Abstract
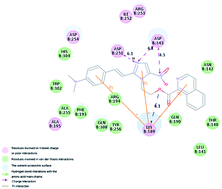
A series of 1-isoquinoline-2-styryl-5-nitroimidazole derivatives has been synthesized and screened for telomerase inhibitory as well as antiproliferative properties on four variant cancer cell lines (U251, Hela, HepG-2 and A549). The bioassay results showed that most of the designed compounds exhibited moderate to potent in vitro inhibitory activity in the enzymatic and cellular assays, of which compounds 3u and 3v were revealed the most potent telomerase inhibitors, with IC50 values of 0.98 μM and 1.92 μM, respectively, compared to staurosporine. Docking simulation was performed to position compounds 3u and 3v into the telomerase active site to determine the probable binding pose. Twenty three compounds were scrutinized by the CoMFA and CoMSIA techniques of 3D Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship (QSAR). These new findings along with molecular docking observations could provide important information that compounds 3u and 3v with potent inhibitory activity in tumor growth inhibition may be potential anticancer agents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...