Facile surface modification of high-voltage lithium-ion battery cathode materials with electroconductive zinc antimonate colloidal nanoparticles
Abstract
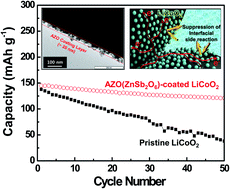
The high-voltage cell approach has garnered a great deal of attention as a simple and effective way to increase the energy density of lithium-ion batteries. Here, we demonstrate a new class of surface modification based on electroconducitve zinc antimonate (AZO, ZnSb2O6) colloidal nanoparticles as a facile and scalable interface engineering strategy for high-voltage cathode materials. The electroconductive AZO colloidal nanoparticles are directly introduced on the surface of cathode materials via simple one-pot solution coating followed by post heat-treatment, in contrast to traditional surface modification using metal oxide precursors that often requires complex sol–gel reaction and high-temperature calcination. LiCoO2 (LCO) powder is chosen as a model cathode material to explore the feasibility of AZO nanoparticle coatings. A salient feature of the AZO nanoparticle layers, as compared to conventional metal oxides-based coating layers that are electrically inert, is the provision of electronic conduction, which thus boosts the electronic conductivity of LCO powders. This beneficial effect of the AZO nanoparticle layers, in collaboration with their contribution to suppressing unwanted interfacial side reactions between delithiated LCO and liquid electrolytes, enables significant improvement in high-voltage (here, 4.4 V) cell performance (AZO nanoparticle-deposited LCO (AZO–LCO) vs. pristine LCO: capacity retention after 50th cycle = 84% vs. 28%, discharge rate capability (2.0 C/0.2 C) = 78% vs. 55%). The potential application of AZO–LCO in high-voltage cells is also discussed with an in-depth consideration of the variation in AC impedance and electrode polarization of cells during cycling.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...