Oxone-mediated oxidative carbon-heteroatom bond cleavage: synthesis of benzoxazinones from benzoxazoles with α-oxocarboxylic acids†
Abstract
A metal-free oxidative cleavage of benzoxazoles using Oxone as an oxidant has been developed. The in situ formed o-aminophenol has been proved to react successfully with α-oxocarboxylic acids affording the benzoxazinones in moderate to good yields.
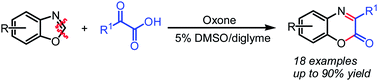

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...