Establishment of two complementary in vitro assays for radiocopper complexes achieving reliable and comparable evaluation of in vivo stability†
Abstract
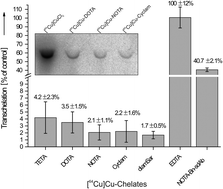
The development of novel radiopharmaceuticals for imaging and therapy requires rapid and reproducible in vitro assays to estimate their in vivo stability and dissociation behaviour. In general, these assays should allow an assessment of dissociation of the radiometal from the radiopharmaceuticals. In the past, a series of chemical challenges has been widely used to estimate complex stability under non-physiological and non-radiotracer conditions providing limited information on the potential in vivo stability. In contrast, we herein present two independent in vitro methods to measure the stability of radiocopper complexes under physiologically relevant conditions. To quantify and compare the dissociation behaviour of six well-established 64Cu chelates (TETA, DOTA, NOTA, Cyclam, diamSar and EDTA), we combine a protein challenge experiment considering the stability of the chelates in the presence of human superoxide dismutase with a serum assay measuring the stability of the radiometal complexes against human serum. Unlike HPLC- and TLC-based analytical techniques, we describe the stability assessments by standard gel electrophoretic procedures, which allow a timesaving workflow as well as simultaneous processing and comparative analysis of a variety of copper-containing chelates and conjugates thereof. [64Cu]Cu-diamSar is the most kinetically stable ligand, whereas the acyclic chelate [64Cu]Cu-EDTA underwent an almost complete complex dissociation. Furthermore, kinetic stability studies in human serum carried out for [64Cu]Cu-diamSar revealed no substantial time-dependent influence under commonly used labelling conditions. Both described assays, the protein challenge experiment as well as the serum stability assay, are not restricted to radiocopper, but may be adopted for other radiometal containing chelates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...