Nanoaggregates of benzothiazole-based amidine-coupled chemosensors: a chemosensor for Ag+ and the resultant complex as a secondary sensor for Cl−†
Abstract
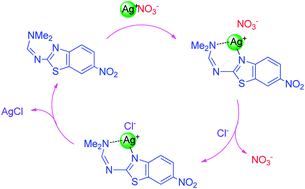
Nanoaggregates of benzothiazole-based amidines were prepared for study as sensors in aqueous medium. Sensor N2 was found to behave as a selective primary sensor for Ag+, and the subsequent complex N2·Ag+ acted as a secondary sensor for Cl− in aqueous medium through a cation displacement mechanism. The cation displacement mechanism was further supported by a CV titration of complex N2·Ag+ with Cl−.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...