Theoretical investigation of vibrational relaxation of highly excited O3 in collisions with HO2
Abstract
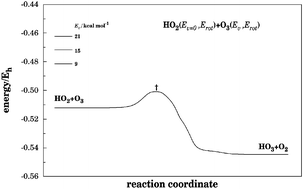
We report calculations of the relaxation process involving highly excited O3 with vibrationally cold HO2. The initial vibrational energies of O3 between 9 and 21 kcal mol−1 are considered. All calculations employ the quasi-classical trajectory method and the realistic double many-body expansion potential energy surface for HO5(2A). Both the traditional histogram boxing and momentum Gaussian binning schemes are utilized in examining the energy transfer process, the latter for the first time in the case of triatomic fragments. The results indicate that it may notable in studying the stratospheric ozone budget.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...