Poly(acrylate) with a tetraphenylethene pendant with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics: highly stable AIE-active polymer nanoparticles for effective detection of nitro compounds†
Abstract
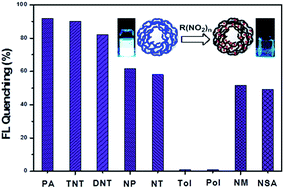
Acrylate monomers with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) attributes were prepared by reacting 4-(1,2,2-triphenylvinyl)phenol with 1-bromoalkan-1-ol, followed by the treatment with acryloyl chloride in the presence of a base. The resulting acrylate monomers were polymerized by free radical polymerization to give very high molecular-weight AIE-active polymers (400 000–650 000) with low polydispersity indices (1.28–1.51). Thermal stabilities of the AIE polymers are comparable to that of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), while their glass transition temperatures are 50–70 °C lower than that of PMMA. The AIE polymers are soluble in common organic solvents and have outstanding film-forming ability. Most importantly, the polymers in the mixtures of THF–H2O can form extremely stable nanoparticles, with no tendency towards agglomeration at 4 °C for over nine months. The polymers exhibit much more significant AIE activity than their monomers and their precursor 4-(1,2,2-triphenylvinyl)phenol in THF–H2O mixtures. Fluorescence of the polymers in THF–H2O mixtures and in the film state can be dramatically quenched by a wide variety of nitro compounds, including picric acid, 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, 2,4-dinitrotoluene, 4-nitrophenol, 4-nitrotoluene, nitromethane and nitrous sulfuric anhydride. The AIE polymers show no response to the reference compounds toluene and phenol. These AIE polymers are thus potential fluorescence sensors for nitroaromatic explosives.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...