Effect of synthetic pathways on the phase transition and side-chain crystallization behavior of alkyl-substituted cellulose ethers
Abstract
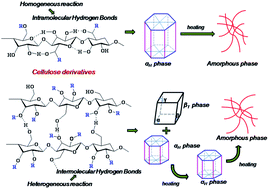
The influence of different synthetic pathways on the phase transition and side-chain crystallization behavior of cellulose ethers was systematically investigated by a combination of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), small and wide-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS, WAXS) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) techniques. DSC investigation indicated that the melting temperature and crystallization temperature, respectively, of cellulose derivatives that were synthesized by homogeneous reactions in cellulose solutions differed from those of cellulose aggregates in a swollen state synthesized by heterogeneous reactions; this implies that the synthetic pathway had a strong effect on the side-chain crystallization behavior in comb-like polymers. WAXS results showed that the cellulose ethers prepared by homogeneous reaction packed into hexagonal crystals, while those prepared by heterogeneous reaction exhibited multiple crystals. These phenomena may be understood as a result of the effect of the regularity of the main chain and the difference in hydrogen bonding interactions in the two kinds of cellulose ethers. For the latter, the presence of free –OH groups at the C-6 position in the samples obtained via the heterogeneous reaction is considered to contribute critically to intermolecular hydrogen bonds that promote crystallization of the system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...