Ceramide synthase inhibitor fumonisin B1 inhibits apoptotic cell death in SCC17B human head and neck squamous carcinoma cells after Pc4 photosensitization†
Abstract
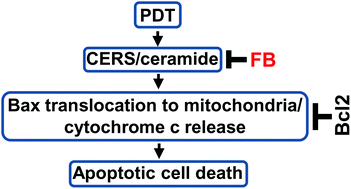
The sphingolipid ceramide modulates stress-induced cell death and apoptosis. We have shown that ceramide generated via de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis is required to initiate apoptosis after photodynamic therapy (PDT). The objective of this study was to define the role of ceramide synthase (CERS) in PDT-induced cell death and apoptosis using fumonisin B1 (FB), a CERS inhibitor. We used the silicon phthalocyanine Pc4 for PDT, and SCC17B cells, as a clinically-relevant model of human head and neck squamous carcinoma. zVAD-fmk, a pan-caspase inhibitor, as well as FB, protected cells from death after PDT. In contrast, ABT199, an inhibitor of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl2, enhanced cell killing after PDT. PDT-induced accumulation of ceramide in the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria was inhibited by FB. PDT-induced Bax translocation to the mitochondria and cytochrome c release were also inhibited by FB. These novel data suggest that PDT-induced cell death via apoptosis is CERS/ceramide-dependent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...