Direct intermolecular C–H arylation of unactivated arenes with aryl bromides catalysed by 2-pyridyl carbinol†
Abstract
Direct intermolecular C–H arylation employing aryl bromide as the arene source has been developed. This process proceeds via a simple transition-metal-free pathway. With the aid of inexpensive and commercially available 2-pyridyl carbinol and potassium tert-butoxide, various unactivated arene C–H bonds can be directly arylated by aryl bromides through homolytic aromatic substitution.
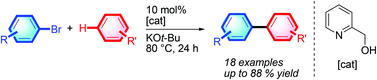

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...