Cooperative hybridization of γPNA miniprobes to a repeating sequence motif and application to telomere analysis†
Abstract
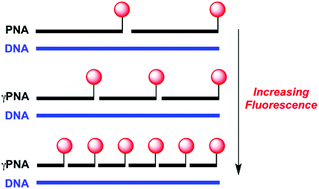
GammaPNA oligomers having one or two repeats of the sequence AATCCC were designed to hybridize to DNA having one or more repeats of the complementary TTAGGG sequence found in the human telomere. UV melting curves and surface plasmon resonance experiments demonstrate high affinity and cooperativity for hybridization of these miniprobes to DNA having multiple complementary repeats. Fluorescence spectroscopy for Cy3-labeled miniprobes demonstrate increases in fluorescence intensity for assembling multiple short probes on a DNA target compared with fewer longer probes. The fluorescent γPNA miniprobes were then used to stain telomeres in metaphase chromosomes derived from U2OS cells possessing heterogeneous long telomeres and Jurkat cells harboring homogenous short telomeres. The miniprobes yielded comparable fluorescence intensity to a commercially available PNA 18mer probe in U2OS cells, but significantly brighter fluorescence was observed for telomeres in Jurkat cells. These results suggest that γPNA miniprobes can be effective telomere-staining reagents with applications toward analysis of critically short telomeres, which have been implicated in a range of human diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...