Palladium-catalyzed regioselective azidation of allylic C–H bonds under atmospheric pressure of dioxygen†
Abstract
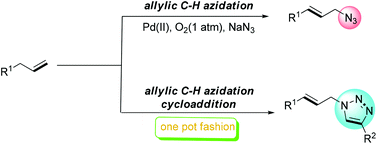
A palladium-catalyzed allylic azidation of alkenes with sodium azide under atmospheric pressure of dioxygen was developed. This methodology provides a new efficient and simple route for accessing allylic azides. Furthermore, the one-pot process consisting of Pd-catalyzed allylic azidation of alkenes and Cu-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition led directly to the 1,2,3-triazole from the alkene. The formed allylic azide can be also in situ reduced to the allylic amine or oxidized to the alkenyl nitrile.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...