Controlled multiple functionalization of mesoporous silica nanoparticles: homogeneous implementation of pairs of functionalities communicating through energy or proton transfers†
Abstract
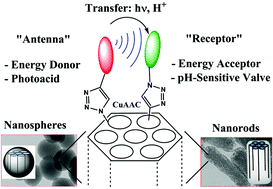
The synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles bearing organic functionalities is strained by the careful adjustment of the reaction parameters, as the incorporation of functional and/or voluminous organosilanes during the sol–gel synthesis strongly affects the final structure of the nanoparticles. In this paper we describe the design of new clickable mesoporous silica nanoparticles as spheres or rods, synthesized by the co-condensation of TEOS with two clickable organosilanes (bearing alkyne and azide groups) and readily multi-functionalizable by CuAAC click chemistry. We show that controlled loadings of clickable functions can be homogeneously distributed within the MSN, allowing us to efficiently click-graft various pairs of functionalities while preserving the texture and morphology of the particles. The homogeneous distribution of the grafted functionalities was probed by FRET experiments between two anchored fluorophores. Moreover, a communication by proton transfer between two functions was demonstrated by constructing a light-actuated nanomachine that works through a proton transfer between a photoacid generator and a pH-sensitive supramolecular nanogate. The activation of the nanomachine enabled the successful release of rhodamine B in buffered solutions and the delivery of doxorubicin in breast cancer cells (MCF-7) upon blue irradiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...