Low affinity binding of plasma proteins to lipid-coated quantum dots as observed by in situ fluorescence correlation spectroscopy†
Abstract
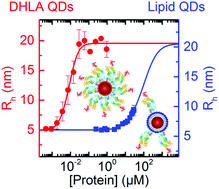
Protein binding to lipid-coated nanoparticles has been pursued quantitatively by using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. The binding of three important plasma proteins to lipid-enwrapped quantum dots (QDs) shows very low affinity, with an apparent dissociation coefficient in the range of several hundred micromolar. Thus, the tendency to adsorb is orders of magnitude weaker than for QDs coated with dihydrolipoic acid.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...