Receptor-mediated membrane adhesion of lipid–polymer hybrid (LPH) nanoparticles studied by dissipative particle dynamics simulations
Abstract
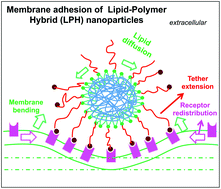
Lipid–polymer hybrid (LPH) nanoparticles represent a novel class of targeted drug delivery platforms that combine the advantages of liposomes and biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. However, the molecular details of the interaction between LPHs and their target cell membranes remain poorly understood. We have investigated the receptor-mediated membrane adhesion process of a ligand-tethered LPH nanoparticle using extensive dissipative particle dynamics (DPD) simulations. We found that the spontaneous adhesion process follows a first-order kinetics characterized by two distinct stages: a rapid nanoparticle–membrane engagement, followed by a slow growth in the number of ligand–receptor pairs coupled with structural re-organization of both the nanoparticle and the membrane. The number of ligand–receptor pairs increases with the dynamic segregation of ligands and receptors toward the adhesion zone causing an out-of-plane deformation of the membrane. Moreover, the fluidity of the lipid shell allows for strong nanoparticle–membrane interactions to occur even when the ligand density is low. The LPH–membrane avidity is enhanced by the increased stability of each receptor–ligand pair due to the geometric confinement and the cooperative effect arising from multiple binding events. Thus, our results reveal the unique advantages of LPH nanoparticles as active cell-targeting nanocarriers and provide some general principles governing nanoparticle–cell interactions that may aid future design of LPHs with improved affinity and specificity for a given target of interest.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...