Conversion of silica nanoparticles into Si nanocrystals through electrochemical reduction†
Abstract
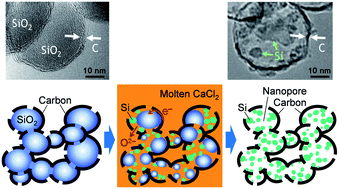
The precise design of Si-based materials at the nanometer scale is a quite complex issue but of utmost importance for their present and potential applications. This paper reports the first attempt to address the electrochemical reduction of SiO2 at the nanometer scale. SiO2 nanoparticles are first covered with a uniform carbon layer with controlled thickness at an accuracy of a few nanometers, by pressure-pulsed chemical vapor deposition. With appropriate thickness, the carbon layer plays significant roles as a current path and also as a physical barrier against Si-crystal growth, and the SiO2 nanoparticles are successfully converted into extremely small Si nanocrystals (<20 nm) inside the shell-like carbon layer whose morphology is derived from the original SiO2 nanoparticles. Thus, the proposed electroreduction method offers a new synthesis strategy of Si–C nanocomposites utilizing the morphology of SiO2 nanomaterials, which are well known for a wide variety of defined and regular nanostructures. Owing to the volume difference of SiO2 and the corresponding Si, nanopores are generated around the Si nanocrystals. It has been demonstrated that the nanopores around the Si nanocrystals are effective to improve cycle performance of Si as a negative electrode for lithium-ion batteries. The present method is in principle applicable to various SiO2 nanomaterials, and thus, offers production of a variety of Si–C composites whose carbon nanostructures can be defined by their parent SiO2 nanomaterials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...