Biocompatible phosphate anchored Fe3O4 nanocarriers for drug delivery and hyperthermia†
Abstract
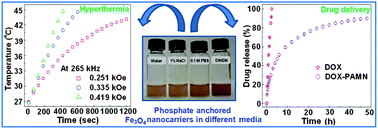
We demonstrate the preparation of biocompatible, water-dispersible phosphate anchored Fe3O4 magnetic nanocarriers (PAMN) by a facile soft-chemical approach. The surface functionalization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles (∼10 nm) with bioactive phosphate molecules (sodium hexametaphosphate) was evident from infrared, thermal and light scattering measurements. These superparamagnetic nanoparticles show better aqueous colloidal stability, good magnetic response and excellent self-heating efficacy under an external AC magnetic field. The bioactive shell not only provides colloidal stability to the particles but also creates functionalized exteriors with high densities of phosphate moieties for conjugation of drug molecules. The drug loading and release behavior of PAMN was investigated using doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) as a model drug to evaluate their potential as a carrier system. The cell viability and hemolysis assay suggests that PAMN do not have adverse toxic effects for further in vivo use. Specifically, high loading affinity for DOX with their sustained release profile and self-heating capacity makes these novel nanocarriers suitable for drug delivery and magnetic hyperthermia.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...