Precursor-driven selective synthesis of hexagonal chalcocite (Cu2S) nanocrystals: structural, optical, electrical and photocatalytic properties†
Abstract
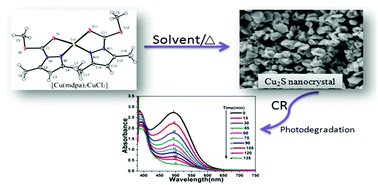
The reaction of CuCl2·2H2O with the methyl ester of 3,5-dimethyl pyrazole-1-dithioic acid (mdpa) yields a blackish brown complex of composition, [Cu(mdpa)2][CuCl2]. The complex formed a well-defined crystal and is characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetry (TG), and spectroscopic studies. The molecule possesses a distorted tetrahedral configuration with a CuN2S2 chromophore with +1 oxidation state of copper. The TG study reveals that the molecule is a suitable precursor for copper sulfide nanoparticles. The low temperature thermal decomposition of the single-source precursor produces hexagonal chalcocite (Cu2S) nanostructures in ethylene diamine and ethylene glycol. A selective synthesis of copper-rich high chalcocite was obtained using the new precursor. The size and morphology of the synthesized Cu2S nanoparticles are guided by the precursor and likely to be less dependent on the solvent used in the experiment. The nanoparticles were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electronic microscope, and UV-Vis spectroscopic studies. The optical band gap of the as-synthesized Cu2S nanoparticles is measured to be 1.80–2.40 eV. The Cu2S nanoparticles are found to be good catalysts in UV photo catalytic decomposition (90%) of Congo red (CR) dye following first-order reaction kinetics, and the reusability study of the Cu2S catalyst also shows excellent catalytic performance (80%).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...