Sensitive and selective electrochemical DNA sensor for the analysis of cancer-related single nucleotide polymorphism†
Abstract
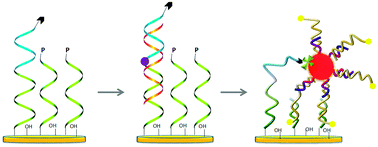
A high-sensitivity and high-selectivity bioassay for single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping is of vital importance for the early diagnosis and effective therapy of many diseases, especially cancer. Here, we developed an electrochemical SNP genotyping sensor for the analysis of a cancer-related gene sequence. To improve the detection sensitivity, an effective signal amplification strategy was developed by combining the gold nanoparticle (GNP)-based enrichment effect with the surface hybridization-based dragging strategy. With the large number of ferrocene (Fc) probes enriched with GNP and then dragged into close proximity to the electrode surface through DNA hybridization, a detection limit at the femtomolar level (4 fM, 40 zmol in 10 μL sample) was achieved with a wide dynamic range (from 10 fM to 1 nM). By using allele-specific nucleotide ligation, high selectivity for specific single point mutations was verified. Moreover, PCR amplicons from both patient samples and standard cell lines have been successfully tested, demonstrating the great potential of this sensing scheme in medical diagnosis of genetic diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...