Fabrication and optical characterization of multimorphological nanostructured materials containing Eu(iii) in phosphate matrices for biomedical applications
Abstract
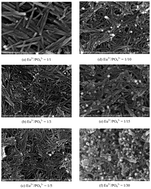
EuPO4·H2O nanorods/nanoparticles with a rhabdophane-type hexagonal form have been successfully synthesized using microwave assisted co-precipitation. The effects of chemical composition and pH on the size, shape, morphology and luminescence properties have been investigated by powder X-ray diffraction, Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM), and photoluminescence spectroscopy. The mean size of the nanorods is about 15–30 nm in diameter and 200–400 nm in length and the size of nanoparticles is 10–20 nm. A powdered sample of these EuPO4·H2O nanorods/nanoparticles emitted yellow-green light with narrow bands at 594, 619, 652, and 697 nm under UV-vis excitation. The surface effects of the built core–shell structure on the fluorescent properties, and the compatibility of the EuPO4·H2O nanomaterials with a biological system, have been studied to develop a new fluorescent label for biomedical imaging. The primary test results in using a EuPO4·H2O–Immunoglobulin G conjugate for recognizing the measles virus in a vaccine is presented.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Advanced Complex Inorganic Nanomaterials

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...