Antitumor properties and mechanisms of mitochondria-targeted Ag(i) and Au(i) complexes containing N-heterocyclic carbenes derived from cyclophanes†
Abstract
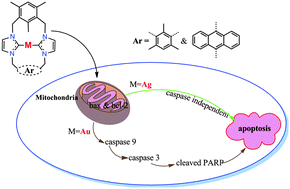
Metal/N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complexes hold great opportunities for the development of novel antitumor metallodrugs. Herein, four Ag(I) and Au(I) complexes containing NHCs derived from cyclophanes have been prepared and characterized as potential anticancer agents. These complexes show higher cytotoxicity than cisplatin against several cancer cell lines including a cisplatin-resistant cell line. The Au(I) complexes display higher anticancer activity than the corresponding Ag(I) complexes. Moreover, all the complexes are less cytotoxic than cisplatin on the normal human liver cell line LO2. Intracellular distribution studies show that these complexes are selectively localized in the mitochondria, especially for the Au(I) complexes. Interestingly, although both Ag(I) and Au(I) complexes can influence mitochondrial integrity, they induce cancer cell death through different mechanisms. The Ag(I) complexes mainly induce caspase- and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-independent early apoptosis. However, Au(I) complexes induce both early apoptosis and late apoptosis through caspase- and ROS-dependent pathways. These studies may open up an avenue for a better understanding of the impact of metal centers on antitumor potentialities and mechanisms.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...