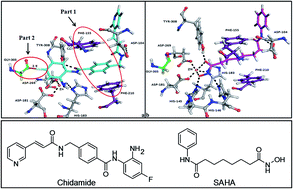
Discovery of an orally active subtype-selective HDAC inhibitor, chidamide, as an epigenetic modulator for cancer treatment†
Abstract
Tumorigenesis is maintained through a complex interplay of multiple cellular biological processes and is regulated to some extent by epigenetic control of gene expression. Targeting one signaling pathway or biological function in cancer treatment often results in compensatory modulation of others, such as off-target drivers of cell survival. As a result, overall survival of cancer patients is still far from satisfactory. Epigenetic-modulating agents can concurrently target multiple aberrant or compensatory signaling pathways found in cancer cells. However, existing epigenetic-modulating agents in cancer treatment have not yet fully translated into survival benefits beyond hematological tumors. In this article, we present a historical rationale for use of chidamide (CS055/Epidaza), an orally active and subtype-selective histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor of the benzamide chemical class. This compound was discovered and successfully developed as mono-therapy for relapsed and refractory peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL) in China. We discuss the evidence supporting chidamide as a durable epigenetic modulator that allows cellular reprogramming with little cytotoxicity in cancer treatments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...