Identification of 2,4-diamino-6,7-dimethoxyquinoline derivatives as G9a inhibitors†
Abstract
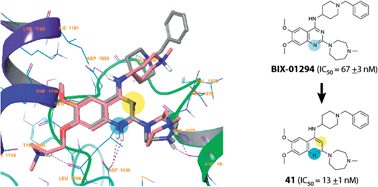
G9a is a histone lysine methyltransferase (HKMT) involved in epigenetic regulation via the installation of histone methylation marks. 6,7-Dimethoxyquinazoline analogues, such as BIX-01294, are established as potent, substrate competitive inhibitors of G9a. With an objective to identify novel chemotypes for substrate competitive inhibitors of G9a, we have designed and synthesised a range of heterocyclic scaffolds, and investigated their ability to inhibit G9a. These studies have led to improved understanding of the key pharmacophoric features of BIX-01294 and the identification of a new core quinoline inhibitory scaffold, which retains excellent potency and high selectivity. Molecular docking was carried out to explain the observed in vitro data.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...