Role of a remote leucine residue in the catalytic function of polyol dehydrogenase†
Abstract
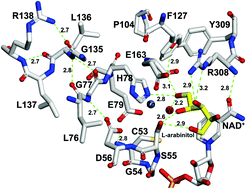
Studies on the protein–metal binding sites have mainly focused on the residues immediately surrounding the reacting substrate, cofactors, and metal ions. The contribution of residues in remote layers to the highly optimized microenvironments of catalytic active sites is not well understood. To improve our understanding, the present study examined the role of remote residues on the structure and function of zinc-dependent polyol dehydrogenases. We used an integrated computational and biochemical approach to determine the role of L136 in the third shell of the L-arabinitol 4-dehydrogenase (LAD) from Neurospora crassa. Substitution of L136 with charged (Asp, Lys, or His) and bulky (Trp) side chain amino acids abolished enzyme activity. Whereas the L136A mutant exhibited a 95% decrease in catalytic efficiency (kcat/Km), the L136C mutant exhibited a 39% decrease in kcat/Km. Additionally, molecular docking and dynamic simulations on the mutant (L136A, L136C, L136H, and L136P) complexes showed the loss of crucial H-bonds between G77 and the corresponding mutated residue. It is evident from theoretical and biochemical studies that the L136 is part of the extensive hydrogen bonding network coupled to the reaction catalyzed at the active site. We propose that L136, critically positioned behind the active site residues H78 and E79 in the third shell of LAD, plays a crucial role in modulating catalysis or substrate binding by stabilizing the GHE motif in the LAD active site.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...