Identification of bacteriophage virion proteins by the ANOVA feature selection and analysis
Abstract
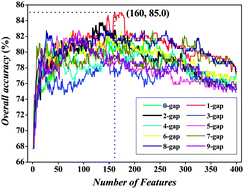
The bacteriophage virion proteins play extremely important roles in the fate of host bacterial cells. Accurate identification of bacteriophage virion proteins is very important for understanding their functions and clarifying the lysis mechanism of bacterial cells. In this study, a new sequence-based method was developed to identify phage virion proteins. In the new method, the protein sequences were initially formulated by the g-gap dipeptide compositions. Subsequently, the analysis of variance (ANOVA) with incremental feature selection (IFS) was used to search for the optimal feature set. It was observed that, in jackknife cross-validation, the optimal feature set including 160 optimized features can produce the maximum accuracy of 85.02%. By performing feature analysis, we found that the correlation between two amino acids with one gap was more important than other correlations for phage virion protein prediction and that some of the 1-gap dipeptides were important and mainly contributed to the virion protein prediction. This analysis will provide novel insights into the function of phage virion proteins. On the basis of the proposed method, an online web-server, PVPred, was established and can be freely accessed from the website (http://lin.uestc.edu.cn/server/PVPred). We believe that the PVPred will become a powerful tool to study phage virion proteins and to guide the related experimental validations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...