Vitreous proteomic analysis of idiopathic epiretinal membranes†
Abstract
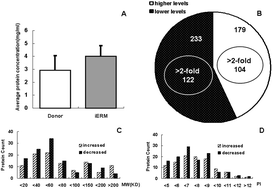
To understand the molecular mechanisms of idiopathic epiretinal membranes (iERMs), the vitreous proteomes of patients with iERMs were investigated. The vitreous proteome in patients with iERMs (n = 8) and donor samples (n = 8) was analysed using reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS) and GeneGo Metacore™. This research followed the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki for the use of human subjects. In this current study, 226 significant changes in protein abundance (abundance ratio >2, p < 0.01) were identified in the vitreous proteome of iERM patients compared to normal control vitreous, including 122 proteins that were present at lower levels and 104 proteins that were present at higher levels. In the iERM vitreous samples, complement components, inflammation-related proteins and matrix metalloproteinase were present at higher levels, while normal cytoskeleton proteins were present at lower levels. The top GeneGo pathway was “immune response”, the top process network was “inflammation”, and the top KEGG pathway was “coagulation cascades”. The essential 2-node proteins of the network were estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1) and p300. Among those found at higher levels, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2O (UBE2O) and complement C4A (C4A) were the most abundant proteins, and could be detected in each of the iERM vitreous samples. It can be concluded that iERMs are a complicated pathological process involving inflammation, immune response, and cytoskeleton remolding. UBE2O and C4A may be candidate biomarkers for iERMs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...