Rapidly improved determination of metabolites from biological data sets using the high-efficient TransOmics tool†
Abstract
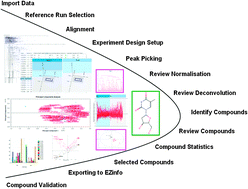
Metabolomics is a new approach based on the systematic study of the full complement of metabolites in a biological sample. Extracting biomedical information from large datasets is of considerable complexity. Furthermore, the traditional method of assessing metabolomics data is not only time-consuming but it is often subjective work. Here we used sensitive ultra-performance LC-ESI/Q-TOF high-definition mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS) in positive ion mode coupled with a new developed software program TransOmics for widely untargeted metabolomics, which incorporates novel nonlinear alignment, deconvolution, matched filtration, peak detection, and peak matching to characterize metabolites as a case study. The TransOmics method can facilitate prioritization of the data and greatly increase the probability of identifying metabolites related to the phenotype of interest. By this means, 17 urinary differential metabolites were identified (less than 10 min) involving the key metabolic pathways including tyrosine metabolism, glutathione metabolism, phenylalanine metabolism, ascorbate and aldarate metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism, and so forth. Metabolite identification has also been significantly improved, using the correlation peak patterns in contrast to a reference metabolite panel. It can detect and identify metabolites automatically and remove background noise, and also provides a user-friendly graphical interface to apply principal component analyses, correlation analysis and compound statistics. This investigation illustrates that metabolomics combined with the proposed bioinformatic approach (based on TransOmics) is important to elucidate the developing biomarkers and the physiological mechanism of disease, and has opened the door for the development of a new genre of metabolite identification methods.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...