NMR- and MS-based metabolomics: various organ responses following naphthalene intervention†
Abstract
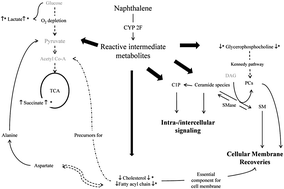
Naphthalene, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, is a ubiquitous environmental pollutant capable of causing illness. In this study, we deconvoluted the metabolites related to naphthalene intervention in various organs by using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Male ICR mice were intraperitoneally dosed with olive oil (vehicle), and a low dose and a high dose (100 and 200 mg kg−1 body wt, respectively) of naphthalene. After 48 h, the lungs, liver, and kidneys were collected for analysing the metabolic responses. The metabolites were extracted and non-targeted profiled using NMR. Low NMR resolution limited the identification of the hydrophobic metabolites. Therefore, LC-MS/MS-based focus lipidomics was applied to profile phosphorylcholine-containing lipids and sphingolipids. Chemometric analysis revealed that succinate and lactate were significantly increased in the lungs, suggesting that energy metabolisms and antioxidation were increased following naphthalene treatment. In the liver, anti-oxidative stress-related metabolites increased, enabling the oxidative stress during naphthalene biotransformation and detoxification to be overcome. The elevation of glutathione protected kidneys from reactive-naphthalene-metabolite-induced injury. Significant alteration of hydrophobic metabolites (membrane constituents) revealed lung and liver were the target organs of naphthalene treatment. MS data demonstrated that phosphatidylcholine (PC) and ceramide species were significantly altered in the lungs and liver, whereas only PC was observed in the kidneys. Elevated numbers of unsaturated bonds and fatty acyl chains in both ceramides and PCs were determined to reduce cellular membrane rigidity and facilitating the trafficking of recovery elements into the cell for rejuvenation. To conclude, the complementary results of NMR- and MS-based metabolomics enabled the characterization of naphthalene-induced changes in various organs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...