Uncovering allosteric pathways in caspase-1 using Markov transient analysis and multiscale community detection†
Abstract
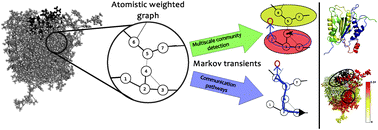
Allosteric regulation at distant sites is central to many cellular processes. In particular, allosteric sites in proteins are major targets to increase the range and selectivity of new drugs, and there is a need for methods capable of identifying intra-molecular signalling pathways leading to allosteric effects. Here, we use an atomistic graph–theoretical approach that exploits Markov transients to extract such pathways and exemplify our results in an important allosteric protein, caspase-1. Firstly, we use Markov stability community detection to perform a multiscale analysis of the structure of caspase-1 which reveals that the active conformation has a weaker, less compartmentalised large-scale structure compared to the inactive conformation, resulting in greater intra-protein coherence and signal propagation. We also carry out a full computational point mutagenesis and identify that only a few residues are critical to such structural coherence. Secondly, we characterise explicitly the transients of random walks originating at the active site and predict the location of a known allosteric site in this protein quantifying the contribution of individual bonds to the communication pathway between the active and allosteric sites. Several of the bonds we identify have been shown experimentally to be functionally critical, but we also predict a number of as yet unidentified bonds which may contribute to the pathway. Our approach offers a computationally inexpensive method for the identification of allosteric sites and communication pathways in proteins using a fully atomistic description.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...