Piper betle leaf extracts induced human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cell death via MAPKs regulating the p73 pathway in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
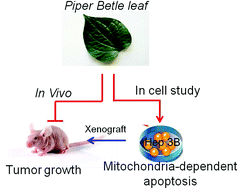
Extracts of Piper betle leaf (PBLs) are rich in bioactive compounds with potential chemopreventive ability. In this study, Hep3B cells which are p53 null were used to investigate the anti-tumor effect of PBLs in the cell and in the xenograft model. The results revealed that PBLs (0.1 to 1 mg mL−1) induced a dose- and time-dependent increase of cell toxicity. The underlying mechanisms as evidenced by flow cytometry and western blot analysis showed that PBLs triggered ATM, cAbl, and p73 expressions and activated JNK and p38 pathways that subsequently led to cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. PBLs also inhibited tumor growth in Hep3B-bearing mice via inducing the MAPK-p73 pathway. Our results demonstrated the in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor potential of PBLs, supporting their application as a novel chemopreventive agent for the treatment of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the future via targeting the p73 pathway.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...