Ashitaba (Angelica keiskei) extract prevents adiposity in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6 mice
Abstract
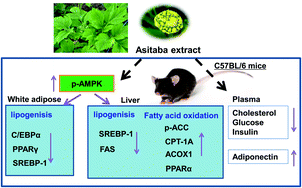
Two main chalcones, 4-hydroxyderricin and xanthoangelol, from Ashitaba, which is a food ingredient and a folk medicine in Asia, have been demonstrated to modulate lipid metabolism in 3T3-L1 and HepG2 cells. In this study, we investigated the effects of Ashitaba extract on adiposity in mice fed a high-fat (HF) diet and its underlying mechanisms based on adipose tissue and hepatic lipid metabolism. C57BL/6 mice were fed a normal or HF diet supplemented with Ashitaba extract (0.01% and 0.1%, w/w) for 16 weeks. Ashitaba extract suppressed the HF diet-induced body weight gain and fat deposition in white adipose tissue, reduced plasma cholesterol, glucose, and insulin levels, increased the adiponectin level, lowered triglyceride and the liver cholesterol content, increased phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in adipose tissue and liver, inhibited lipogenesis in adipose tissue by down-expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) γ, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1), inhibited lipogenesis in the liver by down-expression of SREBP1 and its target enzyme fatty acid synthase, and promoted fatty acid oxidation by up-expression of carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1A and PPARα. In conclusion, Ashitaba extract can possibly prevent adiposity through modulating lipid metabolism through phosphorylation of AMPK in adipose tissue and liver.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...