Si-based Earth abundant clathrates for solar energy conversion†
Abstract
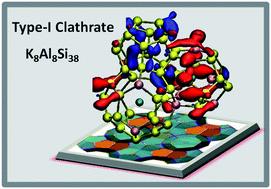
We synthesized a Si-based clathrate, composed entirely of Earth abundant elements, and using ab initio calculations and spectroscopic and Hall mobility measurement showed that it is a promising material for solar energy conversion. We found that the type-I clathrate K8Al8Si38 exhibits a quasi-direct band gap of ∼1.0 eV, which may be tuned to span the IR and visible range by strain engineering. We also found that upon light absorption, excited electron and hole states are spatially separated in the material, with low probability of charge recombination. Finally, we computed and measured electron and hole mobilities and obtained values much superior to those of a-Si and approximately 6 to 10 and 10 to 13 time smaller than those of crystalline Si.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...