Characterization of a meso-chiral isomer of a hexanuclear Cu(ii) cage from racemization of the l-alanine Schiff base†‡
Abstract
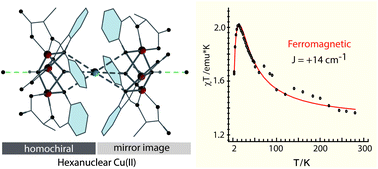
We are reporting structural characterization of two new hexanuclear cages (H3O)2[Cu3(μ3-OH)(μ3-NH3)0.5(L)3]2·8H2O (1) and (H3O)2[Cu3(μ3-OH)(μ3-H2O)0.5(L)3]2·8H2O (1a) where L2− is the dianionic form of the Schiff base of L-alanine and salicylaldehyde. The complex 1 has two C3 symmetric hydroxo bridged trinuclear halves joined by an ammonia or water molecule at the center through H-bonding. Each of the trinuclear halves is enantiopure but of opposite chirality to the other half, making the hexanuclear unit a meso isomer. Temperature dependent magnetic measurements showed the presence of ferromagnetic interactions among trinuclear Cu(II) units, a rare occurrence among trinuclear Cu(II) complexes. Characterization of the LiHL showed it to be enantiopure. Addition of a base, monitored using optical rotation, showed that racemization occurs as a result of base addition. The racemization depends on the base as well as the temperature. Base or Cu(II) induced racemization of amino acid derivatives has been indicated in a number of cases in the past but structural characterization of the products or formation of this type of chiral hexanuclear architecture was never reported. Structures of the complex and the ligand have a number of interesting H-bonding situations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...