α-Radiolysis of ionic liquid irradiated with helium ion beam and the influence of radiolytic products on Dy3+ extraction†
Abstract
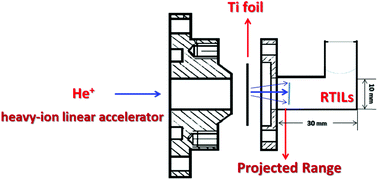
Helium ion (He+) beam produced by a heavy ion linear accelerator was used to simulate α-rays for studying the radiation effect on 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ionic liquid ([C4mim][NTf2]). The water-soluble radiolytic products of [C4mim][NTf2] under He+ beam irradiation were analysed, and it was found that they were similar to those by γ-ray irradiation, but their amount was much less than that by γ-ray irradiation, which was attributed to the recombination of [C4mim][NTf2] radical cations in track by high linear energy transfer (LET) radiations of the He+ beam. The extracting behaviour of Dy3+ using irradiated [C4mim][NTf2] in combination with alkylated bis-triazinyl-pyridine (CA-BTP) was assessed, and found that the influence of He+ beam on the extraction was less than that of γ-ray irradiation. In addition, radiolytic products have a different influence on Dy3+ extraction at different doses; Dy3+ partitioning decreases at 50 kGy due to the protonation of CA-BTP and the inhibition of cation exchange mechanism by radiation-formed hydrogen ions. The abnormal increase of Dy3+ partitioning at 100 kGy is mainly attributed to the precipitation formed between Dy3+ and radiolytic products (F− and SO32−).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...