Influence of riboflavin on the oxidation kinetics of unsaturated fatty acids at the air/aqueous interface revealed by sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy†
Abstract
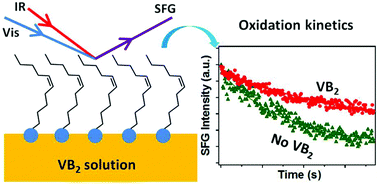
Riboflavin, a common nutrient also known as vitamin B2, is known to potentially play important roles in preventing lipid peroxidations. However, the detailed antioxidant mechanisms, especially the influence of riboflavin on lipid oxidations at biological interfaces, have not yet been fully explored. In the current study, the effect of riboflavin molecules on the oxidation kinetics of monounsaturated cis-11-eicosenoic acid (EA) at the air/water interface was systematically investigated using sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy (SFG-VS). It was discovered that the oxidation rates of the interfacial EA molecules can be reduced by about two to three times in the presence of riboflavin in the aqueous subphase. Further SFG-VS measurements under the protection of nitrogen purging gas showed that more tightly packed and ordered monolayer structures were formed by the surface adsorption of riboflavin molecules, making the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bonds less accessible to the gas phase oxidative species. These results suggested that the antioxidant mechanism for riboflavin in the vicinity of biomembranes may not necessarily involve other reducing agents. They also show the great importance of interfacial molecular structures in biologically relevant chemical reactions.
C bonds less accessible to the gas phase oxidative species. These results suggested that the antioxidant mechanism for riboflavin in the vicinity of biomembranes may not necessarily involve other reducing agents. They also show the great importance of interfacial molecular structures in biologically relevant chemical reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...