Lipid bilayer permeation of aliphatic amine and carboxylic acid drugs: rates of insertion, translocation and dissociation from MD simulations†
Abstract
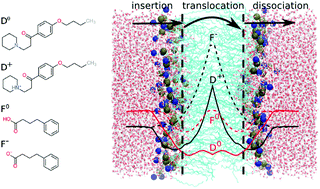
Aliphatic amines (AAs) and carboxylic acids (CAs) constitute the two most commonly occurring chemical groups among orally active drugs [Manallack, et al., ChemMedChem, 2013, 8, 242]. Here, we aim to rationalize this observation in terms of molecular properties that are essential for drug bioavailability. To this end, the permeation of the AA drug dyclonine and the CA drug 4-phenylbutyrate through a lipid bilayer is studied with molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Permeability coefficients for the neutral and ionized forms of these drugs are calculated using the inhomogeneous solubility-diffusion model. To draw conclusions about other AA and CA drugs, the permeability coefficient is expressed as a sum over contributions from drug insertion into, translocation across, and dissociation from the lipid bilayer. Simple but general expressions for each of these separate steps are obtained and validated against the MD simulations of dyclonine and phenylbutyrate. We conclude that the neutral forms of most AA and CA drugs have large permeability coefficients (>1 cm s−1), while their ionized forms ensure solubility in aqueous environments. Thus, a physicochemical rationale for the reported abundance of AAs and CAs among drugs is provided.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...