Design rules for metal binding biomolecules: understanding of amino acid adsorption on platinum crystallographic facets from density functional calculations
Abstract
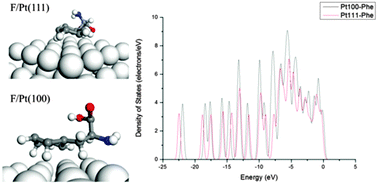
Understanding the mechanism of biomolecules' interaction with inorganic surfaces might pave the way for the design of material interfaces with controlled and highly predictable properties. Here we have focused on the adsorption mechanism of facet-specific amino acids in the sequence of peptides selected for programmed synthesis of Pt(111) and Pt(100) nanocrystals. Using the first principles calculations we have demonstrated that the specific surface recognition of amino acid side chains occurs due to the combination of multiple processes: electron exchange, partial charge transfer and/or dispersive effects providing a high binding affinity to both polar and non-polar residues against both Pt facets. Our approach points towards promising novel routes for controlled design of material-specific linkers for future materials engineering.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...