Formation, isomerization, and dissociation of ε- and α-carbon-centered tyrosylglycylglycine radical cations†
Abstract
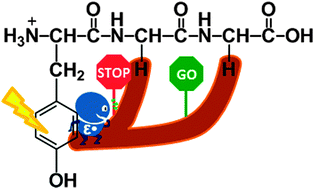
The fragmentation products of the ε-carbon-centered radical cations [Yε˙LG]+ and [Yε˙GL]+, made by 266 nm laser photolysis of protonated 3-iodotyrosine-containing peptides, are substantially different from those of their π-centered isomers [Yπ˙LG]+ and [Yπ˙GL]+, made by dissociative electron transfer from ternary metal–ligand–peptide complexes. For leucine-containing peptides the major pathway for the ε-carbon-centered radical cations is loss of the side chain of the leucine residue forming [YGα˙G]+ and [YGGα˙]+, whereas for the π-radicals it is the side chain of the tyrosine residue that is lost, giving [Gα˙LG]+ and [Gα˙GL]+. The fragmentations of the product ions [YGα˙G]+ and [YGGα˙]+ are compared with those of the isomeric [Yε˙GG]+ and [Yπ˙GG]+ ions. The collision-induced spectra of ions [Yε˙GG]+ and [YGGα˙]+ are identical, showing that interconversion occurs prior to dissociation. For ions [Yε˙GG]+, [Yπ˙GG]+ and [YGα˙G]+ the dissociation products are all distinctly different, indicating that dissociation occurs more readily than isomerization. Density functional theory calculations at B3LYP/6-31++G(d,p) gave the relative enthalpies (in kcal mol−1 at 0 K) of the five isomers to be [Yε˙GG]+ 0, [Yπ˙GG]+ −23.7, [YGGα˙]+ −28.7, [YGα˙G]+ −31.0 and [Yα˙GG]+ −38.5. Migration of an α-C–H atom from the terminal glycine residue to the ε-carbon-centered radical in the tyrosine residue, a 1−11 hydrogen atom shift, has a low barrier, 15.5 kcal mol−1 above [Yε˙GG]+. By comparison, isomerization of [Yε˙GG]+ to [YGα˙G]+ by a 1–8 hydrogen atom migration from the α-C–H atom of the central glycine residue has a much higher barrier (50.6 kcal mol−1); similarly conversion of [Yε˙GG]+ into [Yπ˙GG]+ has a higher energy (24.4 kcal mol−1).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...