Asymmetric bi-layer PFSA membranes as model systems for the study of water management in the PEMFC†
Abstract
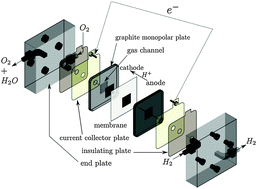
New bi-layer PFSA membranes made of Nafion® NRE212 and Aquivion™ E79-05s with different equivalent weights are prepared with the aim of managing water repartition in the PEMFC. The membrane water transport properties, i.e. back-diffusion and electroosmosis, as well as the electrochemical performances, are compared to those of state-of-art materials. The actual water content (the inner water concentration profile across the membrane thickness) is measured under operation in the fuel cell by in situ Raman microspectroscopy. The orientation of the equivalent weight gradient with respect to the water external gradient and to the proton flow direction affects the membrane water content, the water transport ability and, thus, the fuel cell performances. Higher power outputs, related to lower ohmic losses, are observed when the membrane is assembled with the lower equivalent weight layer (Aquivion™) at the anode side. This orientation, corresponding to enhanced water transport by back-flow while electroosmosis remains unaffected, results in the higher hydration of the membrane and of the anode active layer during operation. Also, polarization data suggest a different water repartition in the fuel cell along the on-plane direction. Even if the interest in multi-layer PFSA membranes as perspective electrolytes for PEMFCs is not definitively attested, these materials appear to be excellent model systems to establish relationships between the membrane transport properties, the water distribution in the fuel cell and the electrochemical performances. Thanks to the micrometric resolution, in situ Raman microspectroscopy proves to be a unique tool to measure the actual hydration of the membrane at the surface swept by the hydrated feed gases during operation, so that it can be used as a local probe of the water concentration evolution along the gas distribution channels according to changing working conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...