Reverse aggregate nucleation induced by acids in liquid–liquid extraction processes†
Abstract
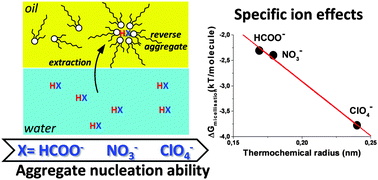
We show in the case of N,N′-dimethyl-N,N′-dioctyl-2-(2(hexyloxy)ethyl)-malonamide (DMDOHEMA) chosen as a typical oil-soluble extractant with surface activity that the free energy of formation of reverse micelles in the solvent phase strongly depends on the presence of polar solutes. Free energies per molecule vary typically from 0 to 2 kT per molecule (5 kJ mol−1), depending on the kosmotropic/chaotropic nature of the anion extracted. Variations of the reverse aggregation free energy introduced by acids and other co-extracted solutes as deduced from the critical aggregation concentrations cannot be neglected while modelling extraction. With typical aggregation numbers of 4–6, the free energy of formation of one reverse aggregate varies up to 20 kJ mol−1, which is four times the typical difference in free energy of one single cation transfer between a “target” and a non-target ion in practical extraction and stripping industrial processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...