On the gas-phase reaction between SO2 and O2−(H2O)0–3 clusters – an ab initio study†
Abstract
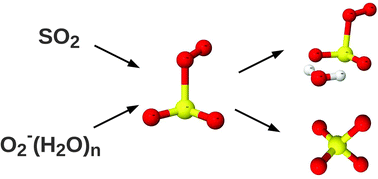
We present an ab initio investigation of the gas-phase reaction between SO2 and a O2−(H2O)n molecular cluster, n = 0–3. The associative product cluster, O2SO2−(H2O)n, is formed with high energy gain although the binding energies decrease with increasing hydration. About 54 kcal mol−1 may be gained by isomerization of O2SO2−(H2O)n to the sulfate radical, SO4−(H2O)n, but a high energy barrier separates the two states. Although the isomerization is catalysed by the presence of a second SO2 molecule, the formation of SO4−(H2O)nvia O2−(H2O)n and SO2 is found to be negligible under atmospheric conditions. At thermal equilibration at 298.15 K and 50% relative humidity the end products are mainly O2SO2− and O2SO2−(H2O)1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...