Nitranilic acid hexahydrate, a novel benchmark system of the Zundel cation in an intrinsically asymmetric environment: spectroscopic features and hydrogen bond dynamics characterised by experimental and theoretical methods†
Abstract
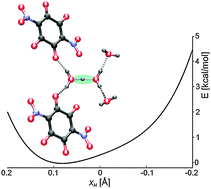
Nitranilic acid (2,5-dihydroxy-3,6-dinitro-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione) as a strong dibasic acid in acidic aqueous media creates the Zundel cation, H5O2+. The structural unit in a crystal comprises (H5O2)2+ (2,5-dihydroxy-3,6-dinitro-1,4-benzoquinonate)2− dihydrate where the Zundel cation reveals no symmetry, being an ideal case for studying proton dynamics and its stability. The Zundel cation and proton transfer dynamics are studied by variable-temperature X-ray diffraction, IR and solid-state NMR spectroscopy, and various quantum chemical methods, including periodic DFT calculations, ab initio molecular dynamics simulation, and quantization of nuclear motion along three fully coupled internal coordinates. The Zundel cation features a short H-bond with the O⋯O distance of 2.433(2) Å with an asymmetric placement of hydrogen. The proton potential is of a single well type and, due to the non-symmetric surroundings, of asymmetric shape. The formation of the Zundel cation is facilitated by the electronegative NO2 groups. The employed spectroscopic techniques supported by calculations confirm the presence of a short H-bond with a complex proton dynamics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...