2 : 1 5-Fluorocytosine–acesulfame CAB cocrystal and 1 : 1 5-fluorocytosine–acesulfame salt hydrate with enhanced stability against hydration†
Abstract
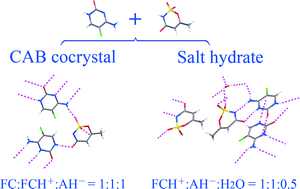
5-Fluorocytosine (FC), a widely used antifungal drug, has poor physical stability under different relative humidity (RH) conditions, which may trigger serious challenges during its drug product development. In this contribution, a conjugate acid–base (CAB) cocrystal and a salt hydrate of FC were obtained with an artificial sweetener, acesulfame (AH), in molar ratios of 2 : 1 (FCAH21) and 1 : 1 (FCAH11), respectively. The resulting products were characterized by a variety of analytical methods, including single-crystal and powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and dynamic vapor sorption (DVS). 13C and 15N solid-state NMR spectra provide solid evidence for the CAB cocrystal/salt formation. At room temperature, moisture sorption data show that the new forms are nonhygroscopic/slightly hygroscopic and resistant to FC hydrate formation under high RH conditions (>80%). FCAH21 has a higher FC content and presents more favorable thermal stability than FCAH11, which make it more attractive for further pharmaceutical application.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...