Halogen-involving weak interactions manifested in the crystal structures of silver(i) or gold(i) 4-halogenated-3,5-diphenylpyrazolato trimers†
Abstract
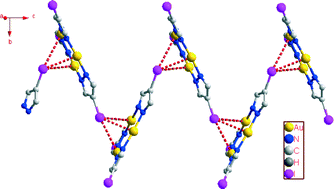
Six triangular silver(I) or gold(I) 4-chloro/iodo-3,5-diphenyl pyrazolates, as well as a triangular silver(I) 4-methyl-3,5-diphenyl pyrazolate, have been synthesized and structurally characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Comparison and inspection of the Ag/Au⋯Cl/I distances, geometries of C–Cl/I bonds with respect to the Ag3 or Au3 triangles, and crystal packing diagrams verify the existence of Ag3⋯Cl/I or Au3⋯I interactions in some of the structures of the trimers, which are strong enough to impart a substantial effect on the spatial arrangement of the trimers in their solid states. Density function theory (DFT) calculations on the trimers give the molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) surfaces and HOMO/LUMOs, which support that the observed M3⋯X structural motifs can be understood on the basis of a weak acid–base interaction having contributions from both ionic δ+⋯δ− attraction and covalent LUMO–HOMO overlap. Calculations also show the existence of the so-called “σ-hole” and the secondary effect to it on the halogen atoms; the structural roles played by them were discussed based on the crystal structures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...