Facile bubble-assisted evaporation-induced assembly of high-density arrays of Co3O4 nano/microlotus leaves: fluorescent properties, drug delivery, and biocompatibility†
Abstract
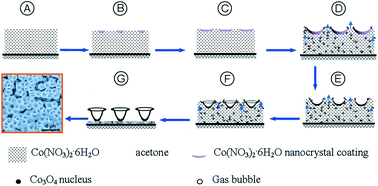
High-density arrays of Co3O4 nano/microlotus leaves with excellent fluorescent properties and biocompatibility were synthesized using a facile bubble-assisted evaporation-induced approach and its potential application in drug delivery was assessed. The morphologically controlled growth of Co3O4 nano/microlotus leaf arrays could be realized by evaporating the acetone solution of cobalt nitrate hexahydrate in a tunable kinetic procedure, in which the gas bubbles generated in situ in the reaction system directed the assembly of the crystal coatings and/or the nuclei. These nano/microlotus leaf arrays were characterized by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nitrogen adsorption/desorption and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) measurements. Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) loaded into these nano/microlotus leaf arrays was used as a model platform to assess the efficacy of the arrays as a drug delivery tool. Its release kinetics study revealed a two-step release pattern of FITC from the nano/microlotus leaf arrays for over 24 h, with a burst release of around 83.4% of the dye just within a few hours. We envision that these Co3O4 nano/microlotus leaf arrays, with the hierarchically porous structures and high efficacy to adsorb chemicals such as the fluorescent dye FITC, could serve as a delivery vehicle for controlled release of chemicals administered into live cells, opening the potential of these arrays for a diverse range of applications including drug storage and release as well as metabolic manipulation of cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...