Programmable protein–DNA hybrid hydrogels for the immobilization and release of functional proteins†
Abstract
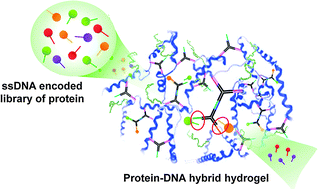
A modular approach for the precise assembly of multi-component hydrogels consisting of protein and DNA building blocks is described for the first time. Multi-arm DNA is designed for crosslinking and stepwise, non-covalent assembly of active proteins inside the hydrogel.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...