Potential-dependent hydration structures at aqueous solution/graphite interfaces by electrochemical frequency modulation atomic force microscopy†
Abstract
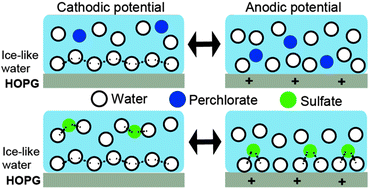
Potential-dependent solvation structures of aqueous electrolyte–graphite interfaces were studied using electrochemical frequency modulation atomic force microscopy. Oscillatory modulations on the force curves reversibly changed with the applied potential on the graphite electrode, and also strongly depended on the anion species in electrolyte solutions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...